The report takes cues from the recovery and reconstruction efforts carried out in other war-torn economies such as Syria, Kosovo, Iraq, Croatia, and Kuwait and offers a robust analytical underpinning for a thorough financial and operational strategy and keen to help Ukraine's early recovery and long-term reconstruction.
The war disrupted global production and trade of commodities across multiple sectors. The war is estimated to have impacted more than 600,000 businesses globally and could slow down the global economic growth by 0.8 percent by the end of 2022 as compared to 2021. The global economy was impacted due to disruptions in production capabilities of both the countries and global supply chains which in turn created a scenario of global inflation.
Impact on global productions
• Due to the war, manufacturers across multiple sectors halted operations in Ukraine as well as Russia
• For instance, automobile manufacturer, Volkswagen, suspended operations in Russia, while automobile parts manufacturer, Sumitomo, shifted production from Ukraine to Romania and Morocco.
Disruption of global supply chains
• Blocking of Ukraine's Black Sea ports and diversion of cargo ships away from Ukrainian ports resulted in supply chain disruptions
• As a result, raw material supplies to car manufacturers all over the world were disrupted
• Fertiliser supplies were also majorly impacted
Rise in commodity prices and inflation
• The war made the biggest impact to commodity markets in nearly 50 years in countries where Ukraine and Russia used to be the major exporters
• With an increase of 154.5 percent, fertiliser prices witnessed the highest increase amongst all the commodities between January-March 2022
• Prices of coal also shot up by 74.7 percent
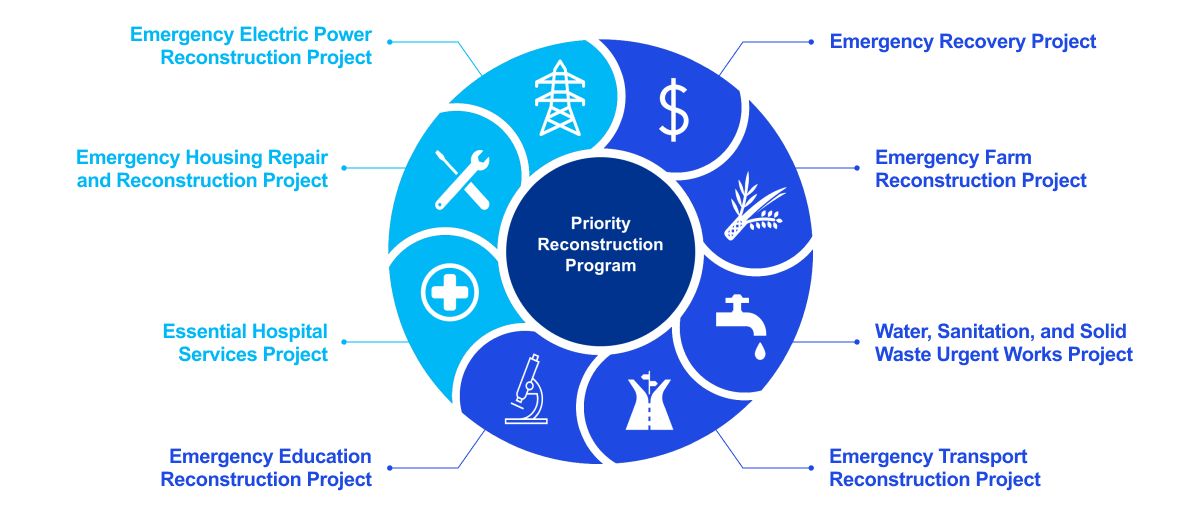
Ukraine’s road to recovery
US$252 billion
- The value of total damages and losses due to the war is estimated to be US$252 billion
- It is further estimated that reconstruction and rebuilding cost could amount to be more than US$349 billion
US$127 billion
- The damages due to destruction of residential and non-residential buildings as of September 2022 is US$127 billion
- Between June and August, the war caused damages worth US$31.5 billion
4.8 million
- Total number of jobs lost in Ukraine since February is 4.8 million
- In the event of the war continuing, even more citizens could lose their jobs and millions could be pushed into poverty, which could counteract the country’s development efforts
Ukraine may follow a similar damage assessment methodology as other war-torn countries followed in the past
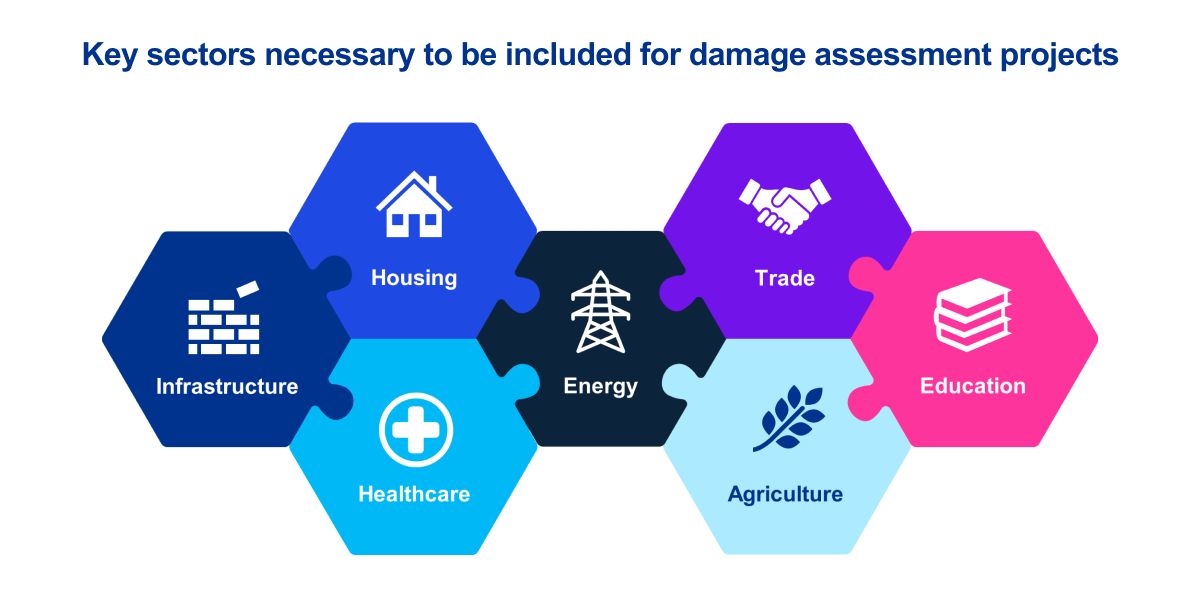
Identification of priority sectors
- Priority economic sectors identified based on the population impacted, factors of production (labor, capital, raw materials and the market for management or entrepreneurial resources), manufacturing capabilities, manufacturing capabilities, exports, imports, contribution to GDP etc.
Assessment of damages and losses
- Assessment of damages and loses across the identified sectors
- The losses take into consideration the changes in economic flows into the priority sectors owing to the war
Estimation of damages, loses and qualitative impacts
- Each sector specified recovery needs are established which includes the cost of reconstruction of the destroyed assets
Damage assessment approach adopted by Syria and Kosovo
Assessment approach in Syria
Remote-based assessment
Six governances and five sectors assessed
Three-phased assessment
- Selection of assessment area: Damage assessment was carried out across six governorate capitals which were selected primarily based on population size
- Identification of priority sectors: Five priority sectors included housing, health, education, transport, and energy
- Three phases of assessment: Pre-war baselines were established in the first phase and in the subsequent phases, quantitative damage assessment was carried out
Assessment approach in Kosovo
Assessment of 14 municipalities conducted
Priority sectors identified
On-ground data collection
- Finalization of assessment area: Initially,14 municipalities were identified for assessment and later, when other areas became accessible, 15 more municipalities were assessed
- Identification of strategic sectors: Key strategic sectors were identified which included housing, healthcare and educational infrastructure, transport, water supply and rural electricity
- Categorization of damage level: Based on the level of damages, educational and healthcare facilities were categorised into four groups
Role of international organisations and other countries in rebuilding economies of war-torn countries
International organisations also play a key role in supporting war-torn countries through monetary, social, and humanitarian aid. As these aspects take a back-seat during the course of armed conflicts, their impact sets in during the later stages of the war, placing the country in a rather desperate situation.
Role of organisations in reconstruction
The World Bank
The World Bank maintains a rather non-political stand and focuses on redeveloping the economy of a war-torn country by prioritising the financial operations of the country through steps such as investment project financing, development policy financing and Program-for-results financing.
European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD)
EBRD’s Resilience and Livelihoods Framework provides assistance to the countries directly affected by war. It focuses on energy security, restoring municipal services and livelihoods for displaced persons, trade finance, and provision of liquidity for small and medium sized enterprises. The Bank has committed up to EUR3 billion over 2022-23 to help restore Ukraine’s businesses and keep the economy functioning.
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund also operates in a similar fashion similar as the World Bank by providing loans to countries in need at concessional rates.
The organisation also aids in the stabilisation of inflation, growth of GDP and stabilise the falling local currency.
War-ravaged countries, in the past have also received aid from other developed countries which played a significant role in the recovery and reconstruction processes.
USAID
In accordance with its United States Foreign Aid program, the US provides aids to its ally countries in form of financial and humanitarian sources. Of late, the middle east countries have been the largest recipient of financial aid by the US.
Iraq received an aid of US$2.5 billion for humanitarian services in 2003 owing to the war it witnessed. This was followed by an aid of US$20.9 billion over a period of three and a half years for Iraq's reconstruction.
European Union (EU)
The European Union (EU) adopts an integrated approach to rebuilding a country affected by wars and crises. It is involved at all stages of a war, from prevention to crisis management and immensely contributes to sustainable peace.
The EU works in close coordination with the member states and effectively combines war prevention, mediation, and peacebuilding.
The EU pledged $US166 million to Iraq since 2016. It is committed to supporting stabilization efforts, bolstering the anti-corruption agenda and strengthening local institutions.
Ukraine can derive insights from the recovery and reconstruction programmes of similar war-torn countries
Although war-torn countries receive aid to overcome the consequences of a war, the journey to becoming a self-reliant nation is a multi-staged and time consuming process.
Croatia’s Social and Economic Recovery Project (CSERP)
Community Investment
- The phase focused on funding goods, works and services for in-demand projects in the Croatian region
Program Management
- This segment of the program focused on addressing social cohesion and economic revitalisation
Demining
- Under the National Mine Action Plan, the stage focused on removing any land mines that had not detonated yet
Institutional Development
- This stage focused on funding consulting services, equipment and capacity building for central, regional, and local authorities
Bosnia and Herzegovina’s recovery program