With a gross domestic product (GDP) of 4.121 billion euros in 2023, Germany is the third-largest economy in the world after the United States and China, and thus also the largest economy in Europe. In particular, the export of motor vehicles and parts as well as chemical products make Germany the third-largest exporting nation in the world. The service sector contributes the largest share to the country's GDP, accounting for 70%.
Data retrieved: April 8, 2024

Leading economic research institutes lower forecast for 2024
In March, leading economic research institutes in Germany drastically revised their forecast downwards. They now anticipane a minimal growth of 0.1%, a stark departure from the 1.3% projection made in the previous autumn. There is currently no growth impetus coming from either Germany or abroad. Domestic private consumption and corporate investment remain tepid, with economic output hovering marginally above pre-pandemic levels. While researchers foresee a gradual recovery starting from the spring, they caution the overall momentum will be modest. In 2024, private consumption is expected to emergeas the most important driving force for the economy, followed by an increase in foreign business anticipated in 2025.
While there was a notable improvement in the companies' business expectations in March 2024, with an increase of 3.1 points according to the ifo Institute, it is still important to note that the index remains relatively low at 87.5 points. This figure contrasts significantly with pre-crisi levels in February 2022, i.e. before Russia's invasion of Ukraine, it was still at 97.9 points.
Our Global Economic Outlook provides insights into global growth prospects, challenges and threats. Our CEO Outlook 2023/24, for which 1,325 CEOs of large companies around the world, including 125 CEOs in Germany, were surveyed, provides assessments of the economic situation, generative AI, ESG and other current topics.
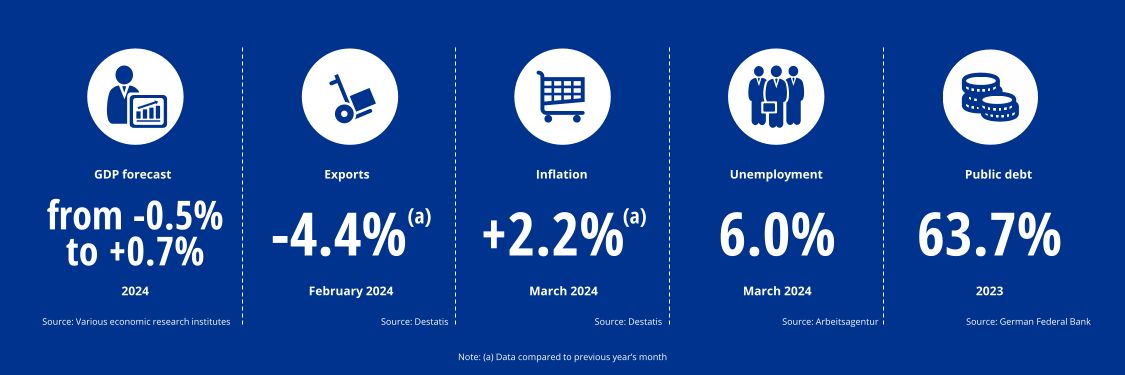
The economic research institutes' current forecasts for GDP growth in Germany vary between -0.5% and +0.7% for the 2024 financial year.

Data retrieved: April 8, 2024

German exports down in February
German exports remain weak. In February 2024, German exports fell by 2.0% compared to January 2024 and by 4.4% compared to February 2023. Conversely, imports rose by 3.2% in February 2024compared to the previous month, though they still lagged significantly behind the previous year’s level by 8.7%. Nevertheless, Germany's export surplus is once again significantly higher than the previous year, primarily due to reduced imports driven by lower energy prices.
Despite the crises in 2024, Germany is poised to achieven an all-time high export surplus. In February 2024, the export surplus of EUR 21.4 billion fell short of January’s record figure of EUR 27.6 billion. However, Germany has already amassed a surplus of EUR 49 billion in the first two months of the year. This represents a significant increase of over 50% compared to the same period last year and even more than double the surplusfrom two years ago. The contribution of foreign trade to Germany's economic output is therefore currently higher again than before the coronavirus pandemic and Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
The mood in the export industry is becoming more optimistic. The export expectations published by the ifo Institute rose to -1.4 points in March, up from -7.0 points in February. Numerous sectors anticipate export growth, with food producers and beverage manufacturers particularly bullish about their prospects. Additionally, there has been a notable shift towards optimism within both the automotive sector and the chemical industry.

Inflation at its lowest level for almost three years
Inflation in Germany continues to fall. In March 2024, consumer prices rose by just 2.2% compared to the same month last year, marking the lowest figure since April 2021, when the inflation stood at 2.0%. In February 2024, the inflation rate was still at 2.5% and in January 2024 at 2.9%.
The decline was primarily attributed to a continued decline in energy prices: These were on average 2.7% lower in March than in the previous year, following a 2.4% decrease in February. Additionally, food prices saw a decrease in March 2024 for the first time since February 2015, falling by 0.7%, following a further increase of 0.9% in February. Services were 3.7% more expensive compared to the previous earlier. Core inflation fell slightly to 3.3%.
Consumers in Germany are hoping that inflation will continue to fall, as fewer companies are planning to raise their prices in the coming months: The ifo Institute's barometer for price expectations fell to 14.3 points in March 2024 (February 2024: 15.0 points), marking the lowest level since March 2021. This metric indicates the percentage of companies intending to increase their prices, with a balance (calculated by subtracting the proportion of companies planning price decreases from those intending increases). If all the companies surveyed intended to increase their prices, the balance would be +100 points. If they all wanted to lower their prices, the balance would be -100.
The economic research institutes' current forecasts for the development of the inflation rate in Germany indicate that the figure will remain at around the current level, fluctuating between +2.2% and +3.5% for the 2024 financial year.

Data retrieved: April 8, 2024

Unemployment rate falls slightly in March
In March 2024, the number of unemployed people in Germany decreased by approximately 45,000 to 2.769 million in March 2024 compared to the previous month. However, this is reflects an increase of 176,000 people compared to March of the previous year. The unemployment rate was 6.0% in March 2024. In March 2023, on the other hand, it was still at 5.7%. The weak economic environment is dampening the overall robust labor market. Although unemployment and underemployment fell in March, the magnitude of the decline was below the usual levels for the month.
Debt ratio falls for the second year in a row in 2023
For the second consecutive year, Germany has seen a decline in its debt ratio, i.e. the ratio of debt to nominal gross domestic product (GDP), reaching 63.7% (2022: 66.3%). However, this is the fourth consecutive year in a row that Germany has exceeded the maximum level of 60% agreed in the European Maastricht Treaty. The last time Germany fell below this mark was prior to the onset of the coronavirus pandemic in 2019, when the debt ration stood at 59.6%. The absolute debt level has also increased by EUR 62 billion euros to EUR 2.6 trillion.
Are you interested in the German market and would like to find out more about Germany as a business location? Stay up to date with our quarterly "Business in Germany" newsletter!
Watch now: Business Location Germany at the KPMG Zukunftsgipfel 2023 (in German) and the International Business Summit 2022
Podcast (in German only)
Your contacts
Stay up to date with what matters to you
Gain access to personalized content based on your interests by signing up today
Andreas Glunz
Managing Partner International Business
KPMG AG Wirtschaftsprüfungsgesellschaft
Joachim von Prittwitz
Markets, International Business
KPMG AG Wirtschaftsprüfungsgesellschaft
Connect with us
- Find office locations kpmg.findOfficeLocations
- kpmg.emailUs
- Social media @ KPMG kpmg.socialMedia





