Connectivity is central to businesses’ ability and opportunity to digitally transform. Just as 3G enabled smartphones and 4G boosted mobile use, 5G provides a massive scaling up of connectivity. It allows broadband and high-speed connective solutions such as the Internet of Things (IoT), high definition streaming, artificial intelligence and virtual reality. With such huge potential to help industry reshape revenue models, optimize operations, and enhance the customer experience, to what extent are Swiss businesses already utilizing 5G or planning to do so in the near future?
5G offers huge benefits over 4G. Not only does it enable many more devices to connect simultaneously to the mobile internet, it also allows up to 100-times quicker download and upload speeds once they are connected. Taken together with edge computing, which moves processing power closer to the user, the benefits are even clearer.
On current wireless networks, data is transmitted from an individual device to a data center to be processed. With edge computing, the data is processed within the device itself. This is critical as use of the IoT grows, such as autonomous vehicles where instant data processing can be invaluable to response speeds. It is also vital in Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication across a vast range of sectors, where vehicles track each other or report live locations to a central point, a vending machine orders refills from a supplier’s system when inventory runs low, or smart meters communicate with a power company’s systems to take current meter readings for energy usage.
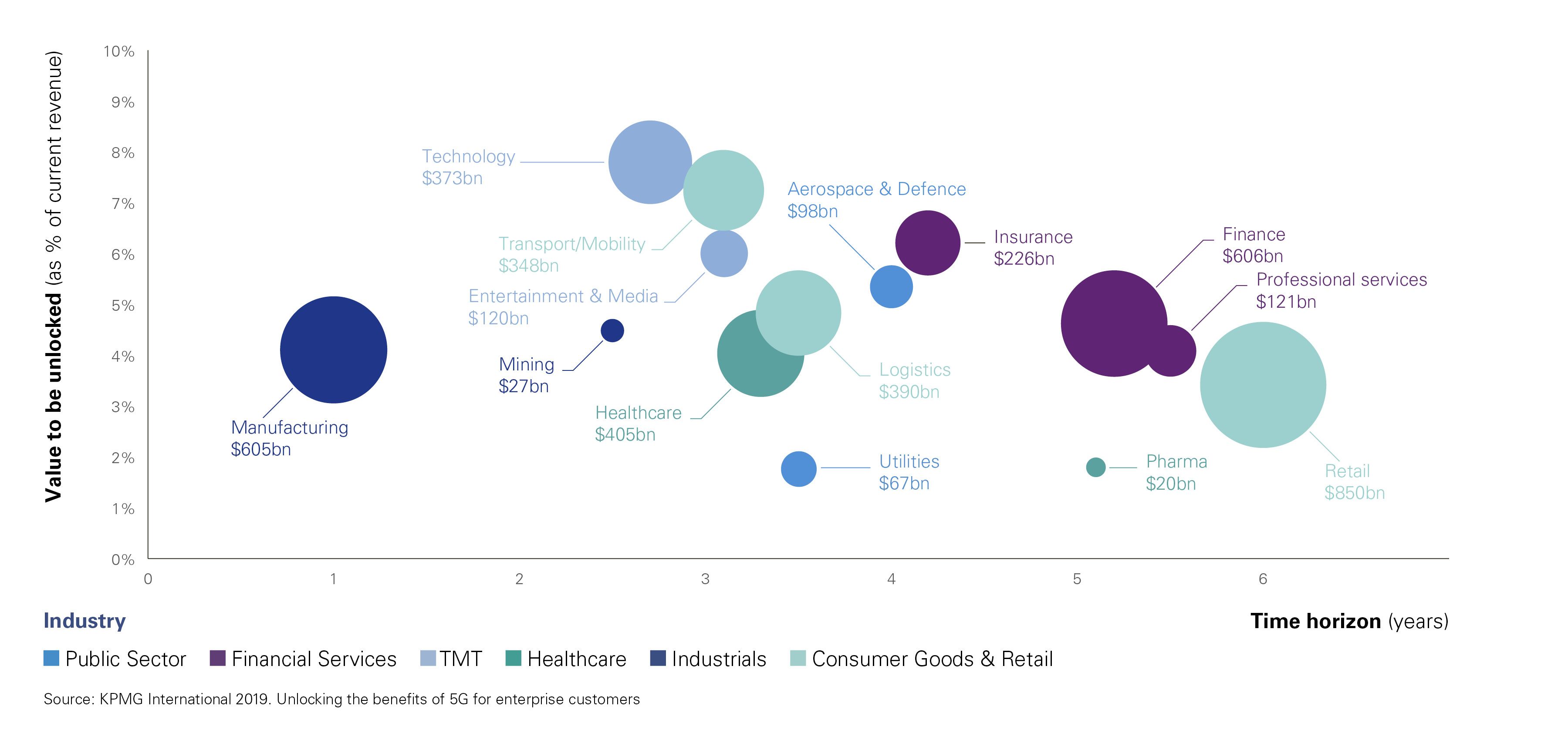
Understanding the scale of 5G’s business potential
KPMG and global market intelligence firm IDC analyzed five sectors: industrial manufacturing, connected healthcare, intelligent transportation, environmental monitoring, and gaming. We estimate that an uptick in adopting 5G and edge computing means that, by 2023, these five industries could drive USD 517 billion in annual revenue into an ecosystem that includes connectivity, hardware, software and services.
Where are solutions already being deployed in Switzerland?
Famous for their innovative capabilities, Switzerland’s businesses are front runners when it comes to the 5G opportunity. We see leading sectors using latest fixed and wireless technology for IoT, including pharmaceuticals, financial services, chemicals, manufacturing, and consumer markets where it has been evident for some time in wearables. Here is a look at three examples:
ABB
Deploying Industrial IoT applications across sectors
Industrial IoT (IIoT) enables data collection and analysis that helps businesses improve operational performance and customer value. By experts having remote access to data and analytics, they can couple their insights with new and emerging technologies to detect issues earlier, diagnose them better, and service them more quickly. ABB applies its expertise across a wide range of industries. For example, ABB embeds remote diagnostics tools onboard vessels to collect and analyze data to be able to promptly detect and correct faults onboard, coordinating equipment diagnostics and recommending preventive maintenance services. These IIOT services help data center operators gain visibility into their own operations and identify issues before they become problems, thereby optimizing energy consumption and operational costs.
As these emerging technologies (5G and Edge) evolve and mature to provide a better IIOT outcome, we as the ABB IT function have to continually re-evaluate and update our connectivity thinking and strategy. And this needs to be done a lot more often nowadays as the landscape both within business and in terms of technology evolution is changing constantly.
Swisscom
Turning data into digital gold
Among a vast range of applications, Swisscom offers IoT Data as a Service. Terming it ‘digital gold’, the company notes how the IoT makes it possible for any company to mine and analyze data and turn it into something profitable. Rhomberg Sersa Rail used a customized IoT solution from Swisscom and Microsoft, for example, to collect, analyze and evaluate positional and operating data from its equipment. The sensor data is transferred to Rhomberg’s Azure IoT Hub via Swisscom to be entered into a database and visualized. The result is insights that enable faster, more cost-effective cross-border workflows.
The IoT is about more than just connecting sensors and devices to the internet. It is about aggregating historic data, publicly available data, and data from other networked ‘things’ to yield insights
Amgen
Leveraging emerging AI to enhance healthcare (Source: 2018 World Medical Innovation Forum)
Biotech company Amgen uses emerging digital capabilities to improve a range of activities, from drug discovery and patient identification, to optimizing interactions with physicians. It leverages two forms of AI – machine learning and deep learning – in several segments. One example is a collaborative pilot program to better diagnose osteoporotic fractures. The training of the machine and deep learning algorithms takes place by exposing the algorithms to very large data sets. In this case, the data sets are many thousands of radiological images. Amgen hopes that this approach will lead to improved diagnosis and ultimately a reduction in secondary fracture risk.
Helping companies move to the next level
A partnership between KPMG and Ericsson focuses on 5G-dedicated networks, with their massive bandwidth and greater reliability and performance. The partnership recognizes the challenge many businesses face in moving beyond the proof of concept (POC) phase in implementing significant change. This is why they have come together to demonstrate how technology can support scale and be used across business, operations and technology.
If you work in industrial manufacturing, for example, you may be looking to enhance your use of Industry 4.0 to increase efficiency and reduce downtime. KPMG and Ericsson have estimated that the use of 5G-dedicated networks - cutting the cable, increasing flexibility and reducing costs – a factory could save USD 1 per square meter per annum. For a plant of 10,000 square meters, that would be a gain of USD 4 million each year. More about this partnership here.
Considerable obstacles yet to be overcome
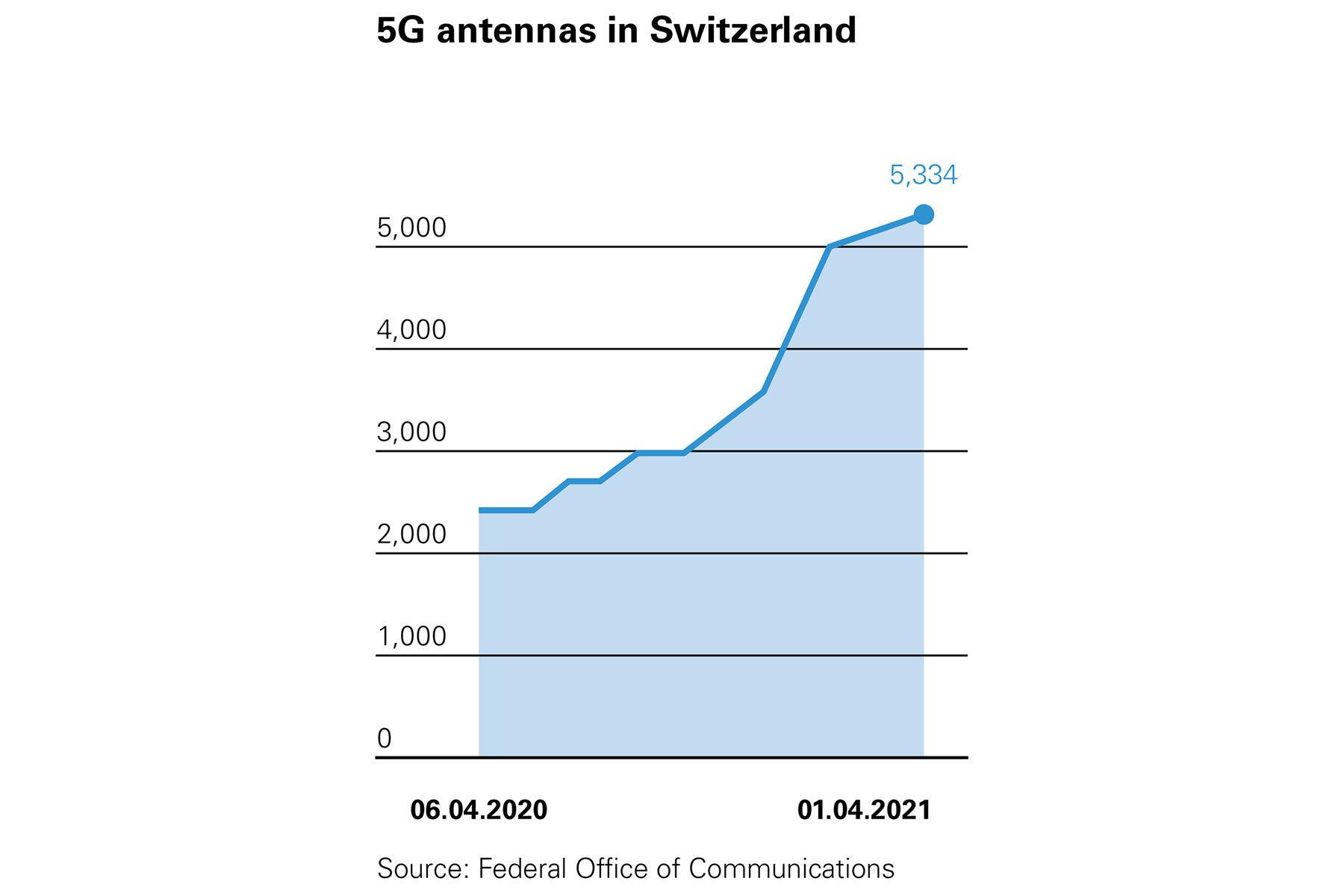
Despite the evident benefits, the 5G rollout in Switzerland is slower than many had expected due to objections around possible health risks. Such concerns have led some cantons to make it more difficult to obtain planning consent for new antennae. This means telecoms providers have focused instead on upgrading existing antennae to 5G. Even here, some cantons have begun to require a planning application. Yet, despite the brakes put on 5G antennae in some more populous cantons including Zurich and Geneva, the past year has seen the number of 5G antennae in Switzerland double from around 2,500 in April 2020 to more than 5,300 in April 2021 («Innert eines Jahres hat sich die Zahl der 5G-Antennen verdoppelt», NZZ am Sonntag, 24 April 2021).
It will be interesting to see if health concerns are allayed, government and cantonal authorities’ positions change, and how the adoption of 5G will compare to Switzerland’s neighbors.
Further risks for IoT implementations
Cyber risk is rated among the highest and most common risks to the success of IoT implementation. The continuous connectivity and uninterrupted sharing of data between machines creates opportunities for cyber crime such as denial of service attacks to disrupt connected businesses, devices being taken over by criminals, and information falsified through spoofing techniques.
Despite the obstacles, we believe that the sheer potential offered by 5G and the IoT means there will be no real let-up in the implementation and adoption of 5G networks. Others agree. The proportion of business-generated data processed outside a traditional centralized data center or cloud is expected to leap from 10 percent in 2018 to 75 percent by 2025.
Preparing for the next leap forward
The combination of 5G, edge computing and the IoT presents enormous potential. It seems clear that they will encourage a leap forward with businesses in Switzerland and abroad deploying these technologies to benefit operational performance and customer delivery.
With this in mind, every board and management team should be asking themselves: What is our 5G strategy? Do we have a roadmap for IoT, and have we identified and mapped the risks? And do we have the right skillsets in-house to implement the necessary change, or do we need support in scaling things up across our business, operations and technology?
Once these questions are answered and the right resources secured, Swiss businesses will be better prepared for the next leap forward and the benefits transformation can bring.
Connect with us
We want to help answer questions. Questions that are currently being asked and questions that may not arise for several days or weeks. Please do not hesitate to contact us – our experts are ready to support you with advice and assistance.